
Long Live the Kings, Seattle, WA
From 2022 – To 2023
Model and report submitted in 2023
The Lake Washington Ship Canal (LWSC) is a vital waterway connecting freshwater Lake Washington (Union Bay) to the saltwater Puget Sound (Shilshole Bay), via the Montlake Cut, Portage Bay, Lake Union, the Fremont Cut, Salmon Bay, and the Hiram M. Chittenden Locks. This engineering marvel, constructed in the early 1900s, supports the region's economic growth and recreational activities.
At the same time, however, the construction of the LWSC and Hiram M. Chittenden Locks (Ballard Locks) fundamentally altered the drainage pattern of the Lake Washington-Cedar-Sammamish watershed and created a pathway for seawater to intrude into the freshwater part of the system. Upon completion of the Ballard Locks, the level of Lake Washington dropped by approximately six feet from its historical water level, and the primary discharge point of the watershed shifted from the Green River-Duwamish River to the Ballard Locks through the LWSC. Consequently, the watershed's salmon, which are anadromous species, must migrate through the Ballard Locks via the fish ladder, smolt flumes, and large or small lock.
The overall objective of this study was to evaluate the hypothesis that cold water supplementation to the LWSC can improve water quality for the benefit of juvenile and adult salmon by using EFDC+, an advanced mechanistic thermal and hydrodynamic model. The study consists of refining an existing 3-dimensional hydrodynamic model of Lake Washington, Lake Union, and the LWSC previously developed by DSI to evaluate the effectiveness of this concept in reducing the potential for heat stress on migrating salmon.
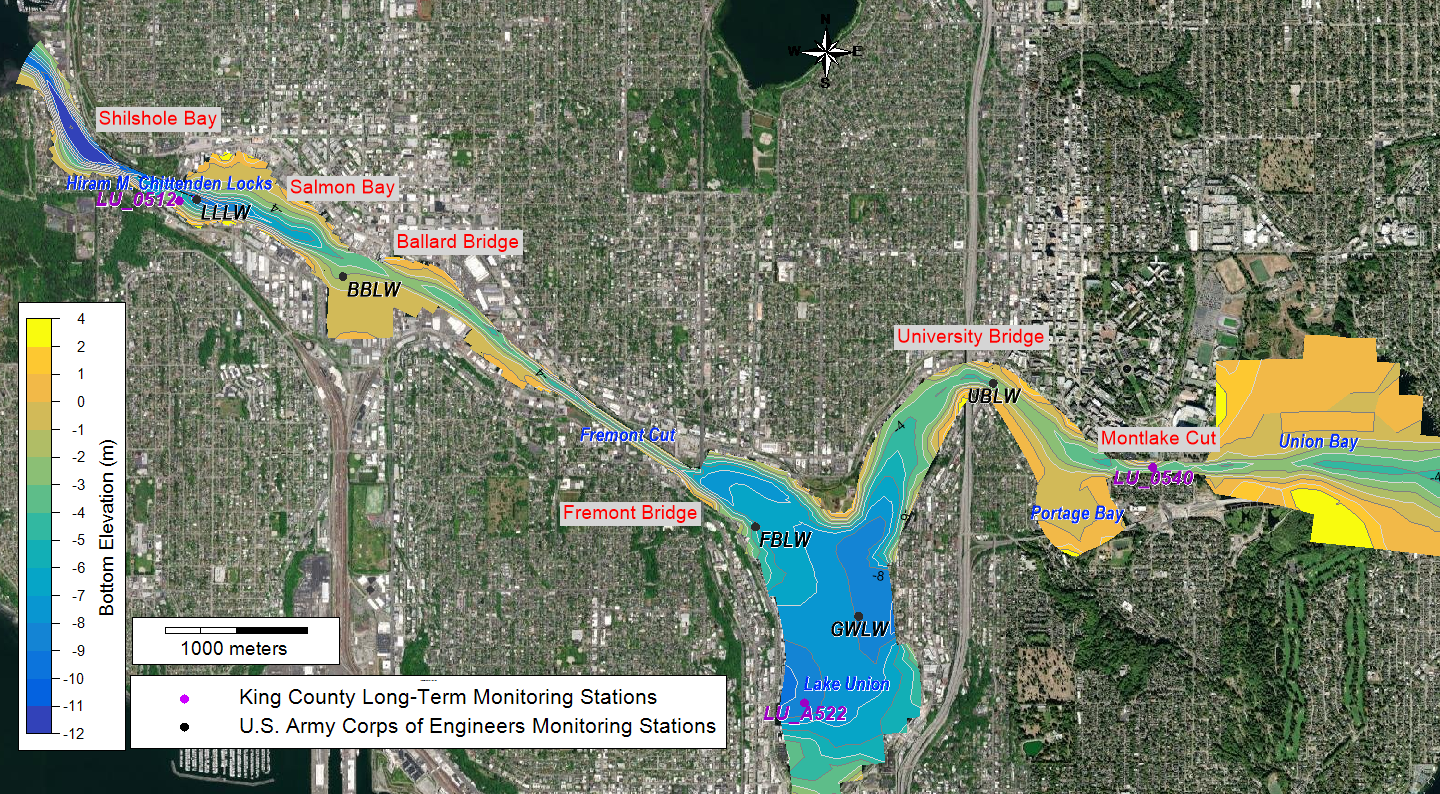
Lake Washington Ship Canal
EFDC+ was used to accurately simulate several alternatives through a collaborative effort among stakeholders. These alternatives focus on seeing the magnitude and extent of cooling that might be achievable through cold water supplementation in the LWSC by extracting water from the colder hypolimnion of Lake Washington and diffusing it into various locations in the ship canal to decrease the potential for highly stressful or lethal conditions for migrating salmon at different life stages.
DSI submitted the final model and report to the client in 2023.